The Role of Cultural Intelligence in Global Careers
Introduction
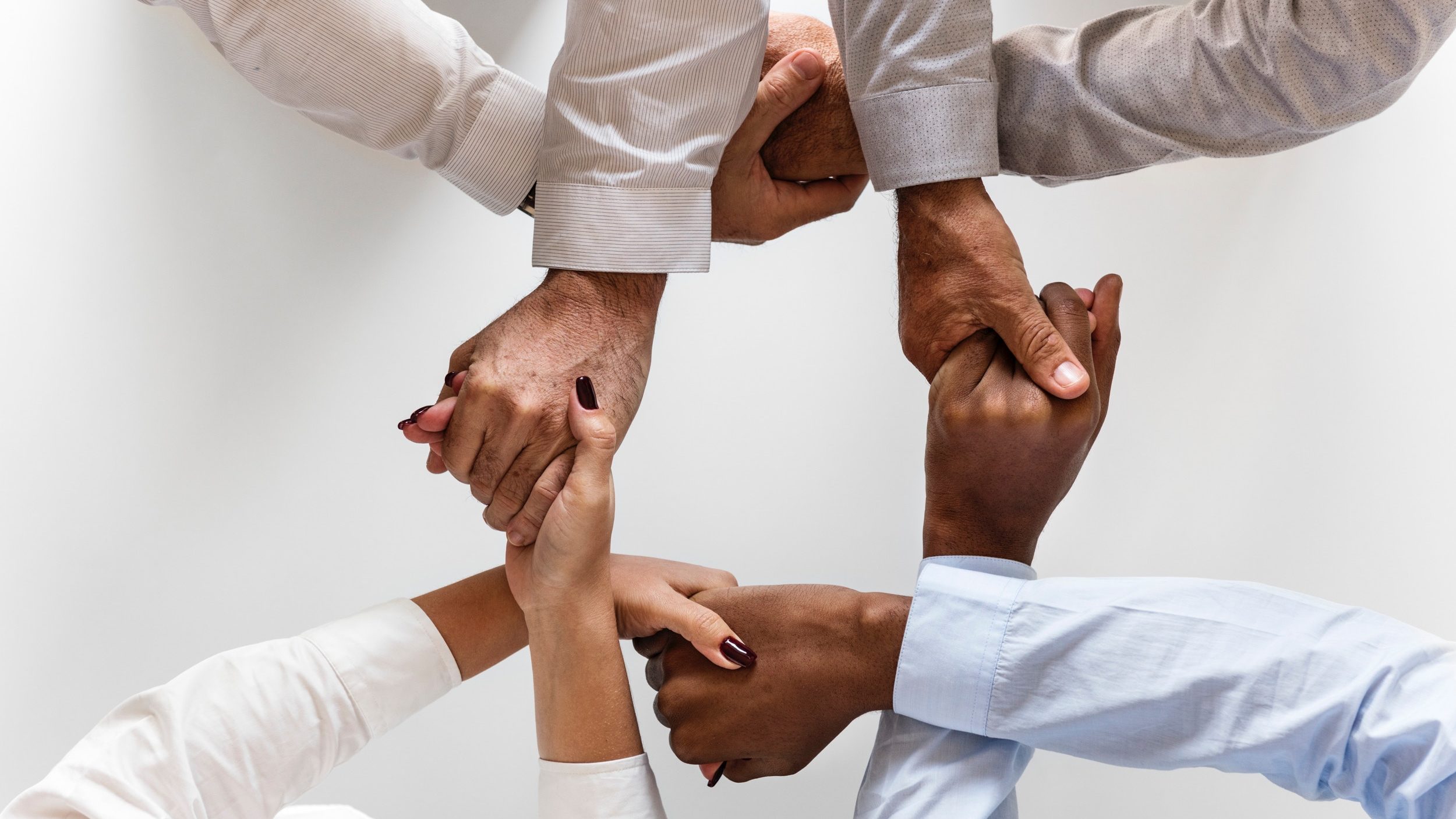
In an increasingly globalized world, the ability to navigate and succeed in diverse cultural landscapes is crucial. Cultural intelligence, often referred to as CQ, plays a pivotal role in shaping successful international careers. This specialized intelligence is not only about understanding different cultures but also about adapting one’s behavior to ensure effective interactions and cooperation across borders. As businesses expand globally and workplaces become more culturally diverse, professionals equipped with high cultural intelligence can significantly leverage their international assignments and opportunities for career advancement. Through understanding and applying cultural intelligence, individuals can enhance their intercultural competence, enabling them to manage and lead more effectively in varied cultural settings.
Understanding Cultural Intelligence
Cultural intelligence (CQ) is a critical capacity for navigating today’s multifaceted global business environment. The concept refers to a person’s ability to relate and work effectively across cultures. Cultural intelligence extends beyond academic intelligence (IQ) and emotional intelligence (EQ) by focusing specifically on the skills and capabilities needed to thrive in new cultural settings. It is rooted in an individualized synthesis of knowledge, practices, orientation, and understanding towards cultural differences and similarities.
Definition of Cultural Intelligence
Cultural intelligence is defined by four interconnected components: cognitive, metacognitive, motivational, and behavioral. Cognitive CQ relates to the knowledge of norms, practices, and conventions in different cultures, which is most often acquired through education and personal experience. Metacognitive CQ involves higher-level thinking strategies that help in acquiring, comprehending, and analyzing cultural situations and issues. Motivational CQ describes the level of interest, drive, and energy to adapt cross-culturally. Lastly, behavioral CQ refers to the ability to adapt verbally and non-verbally with appropriate actions and responses in different cultures.
Importance of Cultural Intelligence in Global Careers
For professionals in international arenas, cultural intelligence fosters job effectiveness. CQ enables individuals to adapt their behaviours to different cultural contexts, aiding in minimization of cross-cultural misunderstandings and enhancing cooperation with diverse teams. Moreover, individuals with high CQ often find better career advancement opportunities as they are able to navigate global markets more adeptly. They effectively lead cross-cultural teams, negotiate complex international deals, and manage overseas assignments. Therefore, developing cultural intelligence isn’t merely an additive skill—it’s a crucial competency for anyone looking to succeed in a global career.
Impact of Cultural Intelligence on Global Career Success
The ability to blend into various cultural contexts—that is, to exhibit high levels of cultural intelligence—can significantly determine the trajectory and achievement in global career landscapes. Professionals who engage and apply cultural intelligence enjoy numerous benefits including better leadership capabilities, enhanced job performance, effective communication, and a broader global network. This overall impact not only advances personal career development but also contributes positively to the organizational success.
Building Cross-Cultural Skills
Building cross-cultural skills involves both training and practical experiences. Here are some tactics to enhance these skills:
– Engage in cultural diversity training: Participate in workshops and seminars that focus on understanding and appreciating cultural differences.
– Learn a new language: Language learning helps to understand not just the linguistic aspects but also the cultural nuance embedded within language.
– Embrace international experiences: Opportunities such as working abroad, international volunteering, or studying internationally can deepen cultural insights.
– Seek out diverse teams: Working in diverse groups enriches understanding through diverse perspectives and experiences.
These activities contribute to a broader appreciation of different cultures, thereby fortifying one’s cultural intelligence.
Enhancing Intercultural Competence
Enhancing intercultural competence involves developing an appreciation for cultural diversity coupled with the ability to perform effectively and appropriately when interacting with others of different cultural backgrounds. Key strategies include:
– Self-awareness: Acknowledge your own cultural bias and understand how it influences behavior.
– Active listening: Pay close attention to and genuinely respect others’ perspectives without imposing your own biases.
– Empathy: Try to emotionally understand the feelings and contexts of other cultures.
– Adaptability: Be flexible in your behavior and attitudes towards cultural differences.
Through concentrating on self-improvement in these areas, individuals can improve their intercultural interactions, crucial for success in global careers.
Overcoming Cultural Barriers in the Workplace
Navigating cultural barriers requires tact, insight, and at times, strategic interventions. Here are some methods to tackle these potential obstacles effectively:
– Promote inclusive leadership: Leaders should encourage inclusivity by modeling acceptance and valuation of cultural diversity.
– Establish clear communication: Misunderstandings can be minimized through explicit instructions and feedback, ensuring clarity.
– Cultivate a supportive environment: Create a workplace atmosphere that respects all cultural backgrounds, promoting open dialogue and mutual respect.
– Conflict resolution: Develop and maintain clear protocols for resolving misunderstandings and conflicts that might arise from cultural differences.
By applying these tools, workplaces can become more accommodating and supportive of cultural differences, thereby improving team cohesion and productivity.
Overall, cultural intelligence is more than an asset—it’s a necessity in our increasingly globalized world. Developing this intelligence and honing necessary skills leads to greater success in international settings, benefiting individuals and organizations alike.
Strategies for Developing Cultural Intelligence
Cultural intelligence, or CQ, is a crucial skill for professionals aiming to excel in a globally interconnected market. Developing this competency involves enhancing one’s understanding, communication, and effectiveness across varied cultural contexts. Here, we explore strategic approaches to nurture and expand one’s cultural intelligence, thereby boosting their global career potential.
Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity Training
Cultural awareness training programs are foundational to building cultural intelligence. These training sessions typically focus on informing individuals about the wide spectrum of cultural norms, values, and practices around the world. The goal is to increase a person’s awareness of cultural differences and, most importantly, teach them how to respond with sensitivity and adaptability in diverse settings. Effective cultural sensitivity training will usually include:
– Interactive Workshops: These involve role-playing scenarios that mimic real-world cross-cultural interactions, encouraging participants to navigate and manage cultural differences actively.
– Educational Seminars: Experts in cross-cultural communication provide insights into global business etiquette, negotiation styles, conflict resolution, and decision-making processes across different cultures.
– Personal Assessments: Tools like the Cultural Intelligence Scale provide feedback on one’s current level of cultural intelligence and highlight areas for improvement.
Such structured programs help individuals recognize their own cultural biases and learn how these biases can impact their interactions. By the end of these sessions, participants are typically better equipped to approach cross-cultural situations with a more open and respectful mindset.
Cross-Cultural Communication Skills
Effective communication across cultures involves more than just translating language. It requires an understanding of nonverbal cues, cultural idioms, and the contextual use of language. Developing strong cross-cultural communication skills can significantly empower individuals to succeed in global careers. Techniques to enhance these skills include:
– Language Learning: While fluency in multiple languages is beneficial, mastering key phrases and understanding linguistic nuances in the primary languages of one’s business contacts can build immense goodwill and foster better relationships.
– Nonverbal Communication Training: Understanding and interpreting body language, gestures, and facial expressions in different cultures can prevent miscommunications and help build rapport.
– Active Listening Techniques: This involves not just hearing but understanding and processing information from another cultural perspective. Active listening also shows respect and encourages more open, productive dialogues.
Regular practice of these skills in varied settings, from formal business meetings to casual social gatherings, ensures that professionals are well-prepared to handle a range of communication challenges in their global interactions.
Exposure to Diverse Cultural Experiences
Real-world exposure to different cultures can be one of the most effective ways to develop cultural intelligence. Immersing oneself in unfamiliar cultural settings enhances empathy, adaptability, and understanding. Strategies to gain this exposure include:
– International Travel: Whether for work or leisure, traveling allows one to experience diverse lifestyles, traditions, and business practices firsthand, providing deep insights that are hard to gain through second-hand information.
– Professional Exchange Programs: Participating in international internships or job assignments offers practical experience in navigating foreign business environments and enhances professional networks.
– Cultural Mentorship: Engaging with mentors from different cultural backgrounds can offer guidance, insights, and feedback on handling cultural differences effectively.
Each of these experiences enriches a professional’s understanding of the world, making them more adept at managing and leveraging diversity for career and business success.
Case Studies of Successful Global Professionals
To illustrate the impact of well-developed cultural intelligence on global careers, consider the real-life stories of several professionals who have excelled internationally by mastering cross-cultural skills.
[Placeholder for Case Study 1: Name and details]
– Background: [Detail the professional’s basic background, including origin and field of work]
– Challenge: [Describe the cross-cultural challenges faced]
– Strategies Used: [List the cultural intelligence strategies employed]
– Outcome: [Share the successful outcomes from applying CQ]
[Placeholder for Case Study 2: Name and details]
– Background: [Detail the professional’s basic background, including origin and field of work]
– Challenge: [Describe the cross-cultural challenges faced]
– Strategies Used: [List the cultural intelligence strategies employed]
– Outcome: [Share the successful outcomes from applying CQ]
These case studies serve as inspiring benchmarks for what can be achieved with commitment to developing cultural intelligence, highlighting not only career advancement but also the personal growth that comes with global success.
By focusing on strategic development of cultural awareness, communication skills, and gaining direct cultural exposure, professionals can enhance their intercultural competence. This not only prepares them to handle the complexities of global business environments effectively but also positions them as valuable assets to any organization looking to strengthen its international presence.
Conclusion: Embracing Cultural Intelligence for a Successful Global Career
In today’s interconnected world, the ability to effectively navigate and thrive in diverse cultures is not just beneficial but essential for career success on a global scale. Cultural intelligence (CQ) stands out as a critical determinant of success in international environments. It enhances communication, fosters respect and understanding, and paves the way for innovative collaboration across geographical and cultural boundaries.
Professionals who invest in developing high CQ can anticipate not only personal growth but also professional advancements in their global careers. They tend to be more adaptable, resilient, and effective in managing complex cross-cultural interactions:
– They tailor communication strategies to fit diverse audiences, ensuring clarity and respect.
– They recognize and respect different working and thinking styles, fostering an inclusive work environment.
– They are capable of overcoming potential conflicts in multicultural settings, turning challenges into opportunities.
Thus, embracing and continually enhancing one’s cultural intelligence is indispensable. It empowers individuals to succeed and lead in global markets, maximizing their impact and effectiveness in diverse settings. For those aiming for the zenith in their international careers, focusing on cultivating deep cultural understanding and adaptability is the key to unlocking a world of opportunities.