The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Management
Introduction
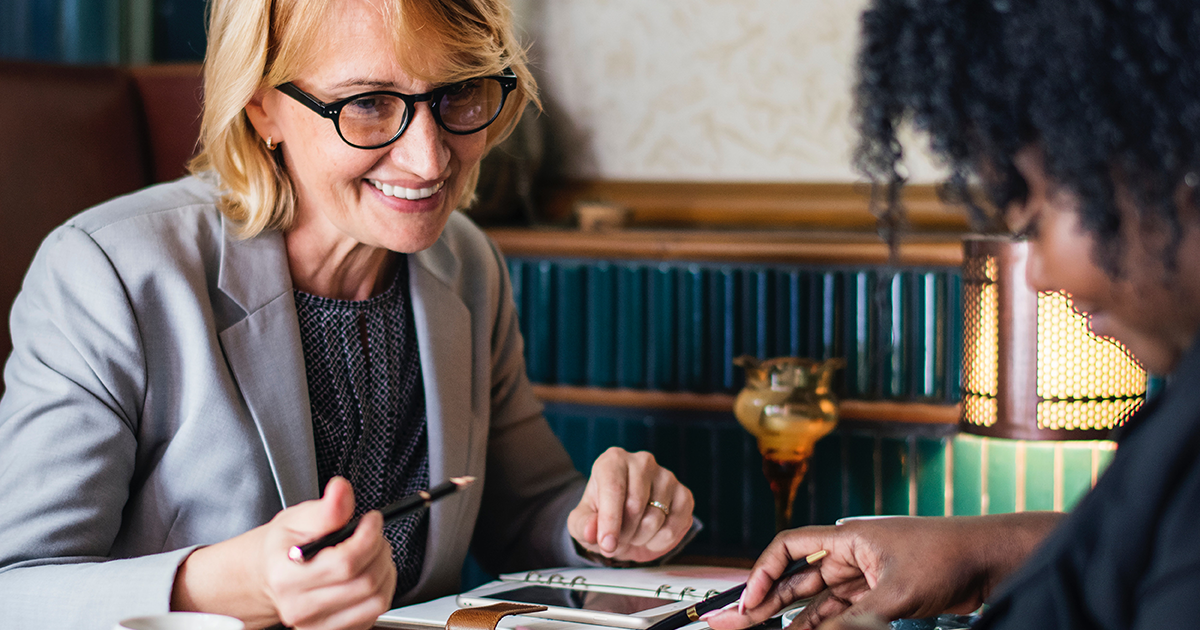
In the contemporary workplace, the ability to navigate conflicts effectively is as crucial as any technical skill. At the heart of adept conflict-management is emotional intelligence (EI), a powerful tool that goes beyond mere reactionary measures. Emotional intelligence is the capacity to understand, use, and manage our own emotions in positive ways to relieve stress, communicate effectively, empathize with others, overcome challenges, and defuse conflict. This ability fundamentally transforms how we interact, leading to healthier and more productive environments. In exploring how EI influences conflict resolution, we will uncover insights into how enhanced interpersonal skills can lead to more effective workplace communication and better overall organizational health.
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Definition of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI), often measured as Emotional Quotient (EQ), refers to the ability to perceive, control, and evaluate emotions in oneself and others. It encompasses several core skills, which are grouped into four main pillars: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. Self-awareness involves recognizing one’s own emotions and their effect on thoughts and behavior. Self-management focuses on managing one’s emotions healthily and constructively. Social awareness refers to understanding the emotions, needs, and concerns of others, while relationship management involves the ability to develop and maintain good relationships, communicate clearly, and influence others.
Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Management
Emotional intelligence is critical in conflict management as it allows individuals to navigate the complexities of interpersonal dynamics effectively. When conflicts arise, high EI can facilitate better communication, foster understanding, enhance problem-solving skills, and promote empathy, enabling individuals to respond rather than react defensively. A well-developed emotional intelligence helps identify not only what one feels but also how others might perceive or react, paving the way for constructive rather than combative exchanges. Here are several ways in which EI proves essential in conflict management:
– Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of another within a conflict can lead to more effective resolution strategies.
– Self-regulation: Keeping emotions in check prevents escalation and maintains a focus on resolution.
– Motivation: Positively influencing others and encouraging a collaborative approach to conflict resolution.
– Social skills: Facilitating better communication and negotiation to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes.
The Connection Between Emotional Intelligence and Conflict Resolution
How Emotional Intelligence Impacts Conflict Resolution
Emotional intelligence profoundly impacts conflict resolution by equipping individuals with the skills necessary to deal with disputes effectively and amicably. Essentially, EI integrates interpersonal and intrapersonal skills that are critical in controlling emotional expressions and developing resilient relationships. High EI in conflict scenarios helps by:
– Enhancing communication: It helps convey messages in a way that is sensitive to others’ emotional states, which is crucial in avoiding misunderstandings and grievances.
– Promoting empathy: This component allows individuals to see the conflict from the other party’s perspective, which can facilitate more empathetic and effective negotiations.
– Aiding emotional management: Managing one’s emotions and understanding emotions expressed by others helps in reducing personal biases and irrational responses.
– Supporting collaborative problem solving: By managing emotions and fostering understanding, EI leads to more collaborative approaches to solving issues, focusing on shared goals rather than individual grievances.
Examples of Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Situations
To illustrate how emotional intelligence facilitates conflict resolution, consider these practical scenarios:
1. A workplace disagreement over project management: An employee perceives that her colleague undermines her input in team meetings. Rather than reacting angrily or becoming defensive, she attempts to understand the colleague’s perspective. Acknowledging her own feelings of inadequacy, she uses EI to regulate her emotions and approaches the colleague privately. They discuss the issue calmly, focusing on how to improve communication and collaboration, which strengthens their future cooperation and team dynamics.
2. Negotiation between departments on resource allocation: The heads of two departments are in conflict over the limited available resources. Each leader uses high EI to express their departmental needs assertively without disrespecting the other’s needs. They employ empathy to understand the opposing constraints and concerns, leading to a compromise where resources are distributed based on urgency of requirements, benefiting the company as a whole.
3. Interpersonal conflict in remote teams: A team leader notices a rising conflict between remote team members due to miscommunications and perceived lack of support. Leveraging his emotional intelligence, the leader arranges a virtual meeting where all parties can express their concerns openly. With a focus on empathetic listening and validating each person’s feelings, the team develops a more effective communication protocol, enhancing collaboration and reducing misunderstandings.
These scenarios demonstrate how EI acts as a linchpin in conflict resolution, fostering environments where constructive dialogue and mutual respect prevail despite differing viewpoints. By prioritizing emotional intelligence, individuals can not only navigate conflicts more successfully but also build stronger, more resilient relationships in all areas of life.
Enhancing Workplace Communication Through Emotional Intelligence
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Effective Communication
Emotional intelligence (EI) is pivotal in shaping interactions within the workplace. It involves the ability to understand, use, and manage one’s own emotions in positive ways to relieve stress, communicate effectively, empathize with others, overcome challenges, and defuse conflict. In a professional setting, this aptitude enhances communication by allowing individuals to convey their thoughts and feelings in a more clear, respectful, and understandable manner. Furthermore, emotionally intelligent employees are adept at reading the emotional cues of their co-workers, which is crucial in adapting their messages and responses to fit the context of the conversation and the emotional state of their audience.
Effective communication often hinges on the ability to connect with others on an emotional level, which can lead to improved cooperation and more productive outcomes. When teams function with a high level of emotional intelligence, misunderstandings are minimized and respect within communication is maximized. This dynamic leads to a more positive work environment, fostering an atmosphere where ideas and feedback can be exchanged more freely and with less risk of conflict.
Moreover, emotional intelligence encourages active listening, a critical component of effective workplace communication. Active listeners pay close attention to what is being said, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as needed, and offering thoughtful feedback. This approach not only helps in resolving issues more efficiently but also builds trust among team members, essential for a collaborative work environment.
Ways to Improve Workplace Communication Through Emotional Intelligence
Improving workplace communication through emotional intelligence can be approached via several practical strategies:
– Self-awareness exercises: Regularly engaging in activities that promote self-awareness can help individuals recognize their own emotional states and how these affect their communication style. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, journaling, and feedback solicitation can cultivate a greater understanding of personal emotions.
– Training sessions: Organizing workshops or training sessions focusing on emotional intelligence can equip employees with essential skills such as empathy, emotional regulation, and active listening. These sessions should also cover how to interpret others’ emotions effectively and respond appropriately in different scenarios.
– Encouragement of feedback culture: Creating a workplace environment that encourages the sharing of honest and constructive feedback can help individuals understand how their communicative approaches are perceived and which areas need improvement. This practice should be framed positively, highlighting it as an opportunity for personal and professional growth.
– Role-playing scenarios: Implementing role-play exercises that simulate challenging communication situations can be an effective way for employees to practice and refine their emotional intelligence skills. These exercises should be guided by experienced moderators to ensure constructive feedback is provided.
– Use of empathy maps: An empathy map is a tool that helps in understanding diverse perspectives during conversations. Employing this technique can assist team members in crafting their messages in a way that resonates well with different audience members.
By integrating these techniques into everyday interactions, organizations can foster a more emotionally intelligent workforce, leading to enhanced communication, reduced misunderstandings, and a more cohesive work environment.
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Empathy, a core component of emotional intelligence, stands as arguably the most significant contributor to effective conflict management and relationship building in the workplace. It involves the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person from their point of view. This not only helps in building strong personal connections but also enables individuals to handle conflicts more compassionately and constructively.
When empathy is present in workplace interactions, employees are more likely to approach disagreements with a mindset geared towards understanding and collaboration rather than contention. Empathetic colleagues treat each other with kindness and respect, striving to understand differing viewpoints and seeking solutions that acknowledge and address each party’s concerns. This approach reduces the likelihood of disputes escalating into serious conflicts and promotes a more harmonious workplace.
Moreover, empathy leads to better customer interactions. When employees exercise empathy with clients or customers, they can more effectively address their needs and resolve any issues, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Furthermore, fostering an empathetic workplace encourages:
– Increased tolerance: Empathy helps individuals recognize the emotional complexities in their coworkers and understand that everyone, at times, can experience stress or irritation. This understanding promotes a more tolerant and supportive workplace atmosphere.
– Enhanced problem-solving abilities: By putting themselves in others’ shoes, employees can often discover novel solutions to problems that benefit all involved parties.
– Stronger leadership: Leaders who exhibit empathy are often more effective because they are viewed as more approachable and understanding. This perception can lead to increased morale and motivation among team members.
In conclusion, emotional intelligence, particularly empathy, plays a critical role in nurturing professional relationships, facilitating effective communication, resolving conflicts, and enhancing overall workplace harmony. Organizations that prioritize these skills among their team members are better equipped to maintain a productive, engaged, and cooperative workforce.
Problem-Solving Skills and Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI) has increasingly been recognized as a pivotal skill set for managing conflicts in both personal and professional environments. At its core, EI involves the ability to understand, use, and manage your own emotions in positive ways to relieve stress, communicate effectively, empathize with others, overcome challenges, and defuse conflict. Problem-solving, a critical aspect of conflict resolution, fundamentally relies on such competencies.
Problem-solving skills enhanced by emotional intelligence include:
– Self-awareness: Recognizing one’s own emotions and their impact on others, which is crucial when identifying the root causes of conflicts.
– Self-regulation: The ability to control or redirect disruptive emotions and impulses and adapt to changing circumstances.
– Motivation: EI drives an individual to pursue goals with energy and persistence, paramount for resolving conflicts where solutions are not readily apparent.
– Empathy: Understanding the emotional makeup of other people. An empathic problem solver can better gauge the emotional state and perspective of others involved in the conflict, leading to more effective resolutions.
– Social skills: Managing relationships to move people in desired directions, whether in leading, negotiating, or working as part of a team.
By integrating these EI competencies, individuals can approach conflicts not merely as obstacles but as opportunities to improve understanding, growth, and interpersonal dynamics critical for lasting solutions.
Application of Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Management
Emphasizing emotional intelligence in conflict management involves understanding and applicating EI principles to enhance interpersonal interactions and resolve disagreements. The application of EI can transform potential confrontations into avenues for fostering mutual respect and understanding, thereby enhancing overall communication and collaboration.
Strategies for Using Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Resolution
Implementing emotional intelligence in conflict resolution requires deliberate strategies that leverage EI skills to manage and resolve conflicts effectively. Some of these strategies include:
– Active Listening: Engage actively in listening to understand all parties’ perspectives without prematurely passing judgment. This helps in acknowledging emotions involved, not just words.
– Expressing Empathy: Demonstrating understanding of others’ feelings and views helps in building trust and respect. It can significantly lower barriers and resistance between conflicting parties.
– Regulating Emotions: Keeping your emotions in check can prevent escalation of conflict. It’s essential to remain calm and composed, demonstrating a non-threatening stance.
– Seeking Feedback: Understanding how others perceive your actions and words can enlighten you on potential improvements or adjustments needed in your approach.
– Encouraging Open Communication: Promote an environment where all parties feel safe to express their thoughts and emotions. This openness can lead to more comprehensive and enduring solutions.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can harness their EI to navigate through conflict more effectively, making resolutions more achievable and sustainable.
Benefits of Applying Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Management
The application of emotional intelligence in conflict management extends its benefits beyond just resolving the issue at hand. These benefits enhance both personal growth and professional productivity amongst individuals in a workspace. Key benefits include:
– Enhanced Team Cohesion: High EI contributes to better understanding among team members, fostering a supportive and collaborative work environment.
– Improved Communication: EI promotes clearer and more effective communication, reducing misunderstandings and misinterpretations that can often escalate conflicts.
– Greater Leadership Effectiveness: Leaders with high EI are better equipped at managing diversity, leading change, and resolving conflicts, which are critical components in dynamic work environments.
– Increased Stress Management: Better handling of emotions contributes to lower stress levels, even in challenging situations, ensuring individuals remain productive and focused.
– Higher Job Satisfaction and Retention: Workplaces that cultivate and employ EI principles tend to have higher satisfaction and retention rates as employees feel valued and understood.
In conclusion, emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in not only managing and resolving conflicts but also in fostering an environment conducive to collaborative and progressive interactions. As organizations and individuals strive to improve their conflict management capabilities, focusing on enhancing emotional intelligence can provide significant leverage in achieving more harmonious and productive outcomes.
Improving Interpersonal Relationships Through Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EI) plays a crucial role in developing and enhancing interpersonal relationships, especially in conflict-prone environments like the workplace. Individuals with high EI are adept at identifying and managing not only their own emotions but also the emotions of others, facilitating improved understanding and cooperation.
Awareness and Regulation of Emotions
At the core of EI in interpersonal relationships is the ability to be aware of one’s own emotions and to regulate them effectively. This self-awareness allows individuals to approach interactions from a place of calmness and clarity, rather than reactivity. For instance, during a heated discussion, an EI-equipped individual will recognize feelings of anger or frustration rising and will use strategies such as deep breathing or pausing to think to regulate these emotions.
Self-regulation also extends to recognizing when to express emotions and when it might be wiser to hold back. By managing their emotional responses, individuals can avoid escalation of conflicts and maintain a constructive dialogue.
Empathy and Understanding Others
Another crucial aspect of EI is empathy, the ability to understand and share the feelings of another. This skill is invaluable in resolving conflicts as it fosters a deeper mutual understanding and respect between parties. In the workplace, empathetic individuals are those who can:
– Listen actively to co-workers, without immediately forming judgements or interrupting.
– Put themselves in others’ shoes, which helps in understanding not just the what and how, but the why behind their peers’ actions or reactions.
– Respond appropriately, showing that they value the perspectives and feelings of others, which can defuse potential conflicts and build trust.
Effective Communication
Enhanced EI contributes to more effective communication, which is essential in maintaining productive interpersonal relationships. Communication in this context goes beyond mere verbal exchange; it involves non-verbal cues, listening skills, and the ability to convey respect and understanding even under stress. High EI helps in:
– Choosing words carefully to avoid misunderstandings or offensive tones.
– Detecting and interpreting non-verbal signals from others, which often reveal more about their true feelings than words do.
– Maintaining eye contact and showing attentiveness, which conveys respect and interest in the conversation.
By integrating emotional intelligence into their day-to-day interactions, individuals can significantly improve how they connect with others in the workplace. It leads not just to reduced instances of conflict but also to more collaborative and supportive work environment.
Conclusion
In summary, emotional intelligence plays a pivotal role in conflict management and resolution within the workplace. The ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions enhances interpersonal skills, facilitating more effective communication and negotiation during disputes. By fostering emotional awareness and empathy, individuals can better navigate conflicts, leading to healthier work environments and more productive outcomes.
– Emphasizing the importance of self-awareness in understanding personal triggers and responses.
– Highlighting empathy towards others to foster mutual respect and understanding.
– Stressing the need for active listening to ensure all parties feel heard and valued.
The benefits of integrating emotional intelligence into conflict management strategies are clear. It not only helps in resolving immediate disputes but also builds a foundation for long-term collaborative relationships, ultimately driving organizational success.